Cumulative preference share helps the company raise funds, and it is a financial instrument because it carries the nature of equity and debt. Assume that company ABC has five million ordinary shares and one million preferred shares outstanding. The company pays dividends to common shareholders every other year, while preferred shareholders are guaranteed a $3 dividend per share. Similarly, any dividends in arrears due to the owners of preferred shares must be paid in full before the board considers paying a dividend on common shares. A board of directors can vote to suspend dividend payments to owners of shares, preferred or common.
Common Shares Vs. Preferred Shares
- Assume that company ABC has five million ordinary shares and one million preferred shares outstanding.
- They turn into outstanding dividends that the company owes to its shareholders, especially those holding preferred shares.
- The impacts that any further or escalating geopolitical conflicts will have on our business is uncertain and difficult to predict.
- At the same time, it is beneficial for the company that does not require to pay every year compulsorily.
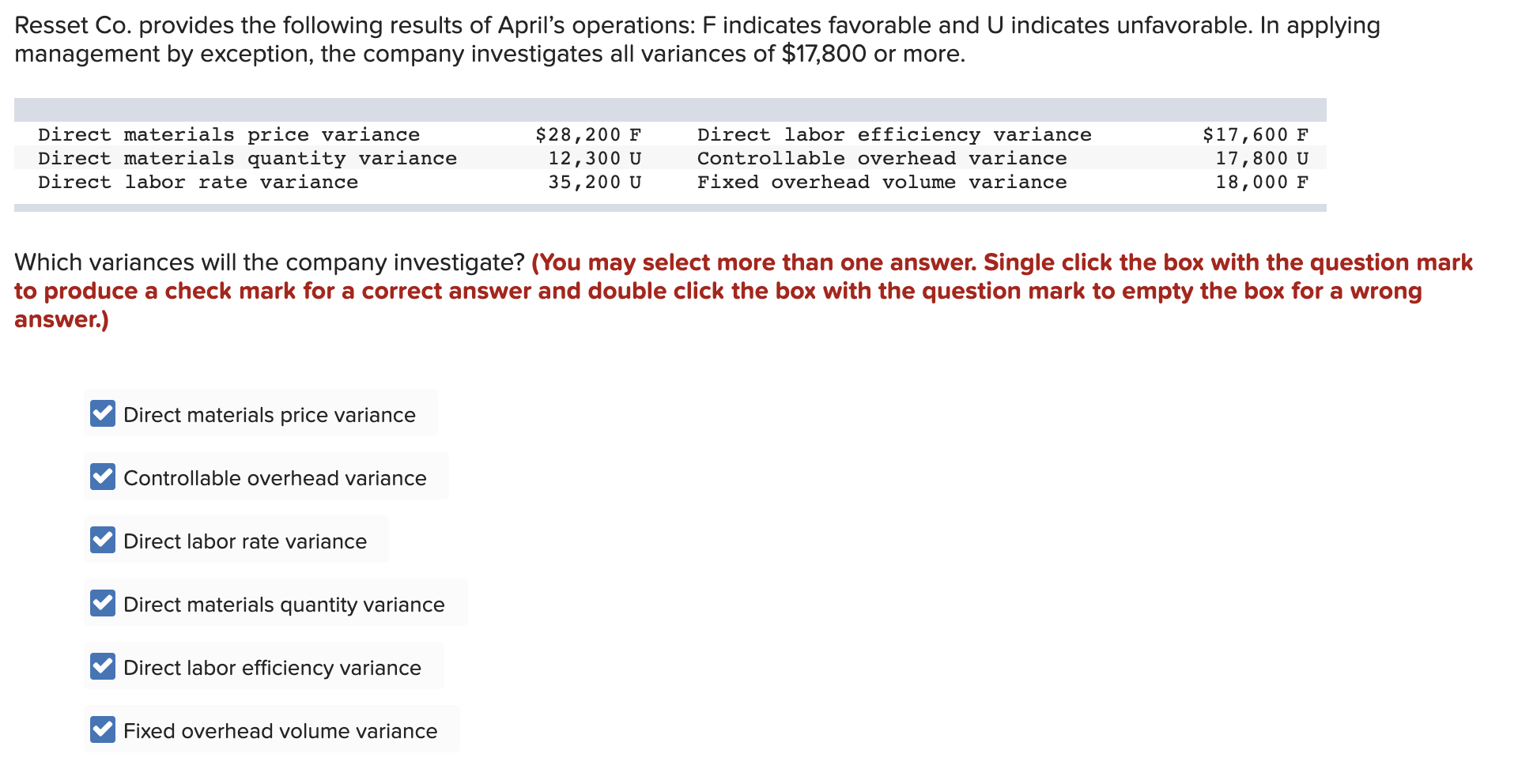
MCAN also qualifies as a mortgage investment corporation (“MIC”) under the Tax Act. MCAN is the largest MIC in Canada and the only federally regulated MIC. There can be no assurance that such expectations, estimates, projections, assumptions and beliefs will continue to be valid. The impacts that any further or escalating geopolitical conflicts will have on our business is uncertain and difficult to predict. Preferred stock is often compared to bonds because both may offer recurring cash distributions.
Cash Dividends on the Balance Sheet
Cumulative preferred stock is a type of preferred stock; others include non-cumulative preferred stock, participating preferred stock, and convertible preferred stock. It also shows an obligation that needs settling before any profits can be shared with common shareholders. Next, let’s look at how companies handle paying out dividends when there are accumulated arrears.
Dividends in arrears on cumulative preferred stock: what does this mean?
Julia Kagan is a financial/consumer journalist and former senior editor, personal finance, of Investopedia. These companies have increased their dividends every year for 50+ years. However, any further disclosures made on related subjects in subsequent reports should be consulted. 2 These measures have been calculated in accordance with OSFI’s Leverage Requirements and Capital Adequacy Requirements guidelines. Complete copies of the Company’s 2024 Third Quarter Report will be filed on the System for Electronic Document Analysis and Retrieval (“SEDAR+”) at and on the Company’s website at Pete Rathburn is a copy editor and fact-checker with expertise in economics and personal finance and over twenty years of experience in the classroom.
In many ways, preferred stock share similar characteristics to bonds, and because of this are sometimes referred to as hybrid securities. This determines whether preferred shares will receive dividends in arrears, which is payment for dividends missed in the past due to inadequate amount of dividends declared in prior periods. If preferred stock is non-cumulative, preferred shares never receive payments for past dividends that were missed. If preferred stock is cumulative, any past dividends that were missed are paid before any payments are applied to the current period.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
Like bonds, preferred shares appeal to a more conservative investor, or they comprise the conservative portion of an investor’s diverse portfolio. This may be a set percentage or the return may fluctuate with a certain economic indicator. For further details, refer to the “Non-GAAP and Other Financial Measures” section of this new release. Non-GAAP and other financial measures and ratios used in this document are not defined terms under IFRS and, therefore, may not be comparable to similar terms used by other issuers. MCAN employs leverage by issuing term deposits that are eligible for Canada Deposit Insurance Corporation deposit insurance.
Therefore, the amount of these past omitted dividends that remain unpaid must be disclosed in the notes to the financial statements. The past omitted dividends on the cumulative preferred stock are referred to as dividends in arrears. Cumulative preferred dividends go from being a balance sheet footnote to a recognized liability when your board of directors declares a dividend.
Preferred shareholders have an advantage; they receive dividend payments before common shareholders. Unpaid dividends become dividends in arrears after a company skips or delays their payment beyond the scheduled date. They turn into outstanding dividends that the company owes to its shareholders, especially those holding preferred shares. These examples show how easily missed or suspended dividend payments can lead to significant obligations over time – obligations which could influence a company’s future financial strategies and shareholder satisfaction. Dividends in arrears are a cumulative amount of unpaid dividends of past years payable on cumulative preference shares only.
Preferred share dividends, like bond rates, are largely influenced by the interest rates set by the Federal Reserve at the time they are issued. Companies that issue callable shares retain the option to repurchase existing preferred shares and reissue them with a lower dividend rate when what are manufacturing costs interest rates fall. However, preferred shareholders have a higher claim on company assets in the event of bankruptcy. This is not especially meaningful since even preferred shareholders are in line for repayment behind secured creditors, unsecured creditors, and tax authorities.